Data literacy is one of the important concepts in modern society.
Simply put, data literacy refers to the ability of individuals or organizations to collect, understand, interpret, and utilize data.
Data literacy is consist of 'Reading Data', Working with Data', and 'Communicating with Data'.
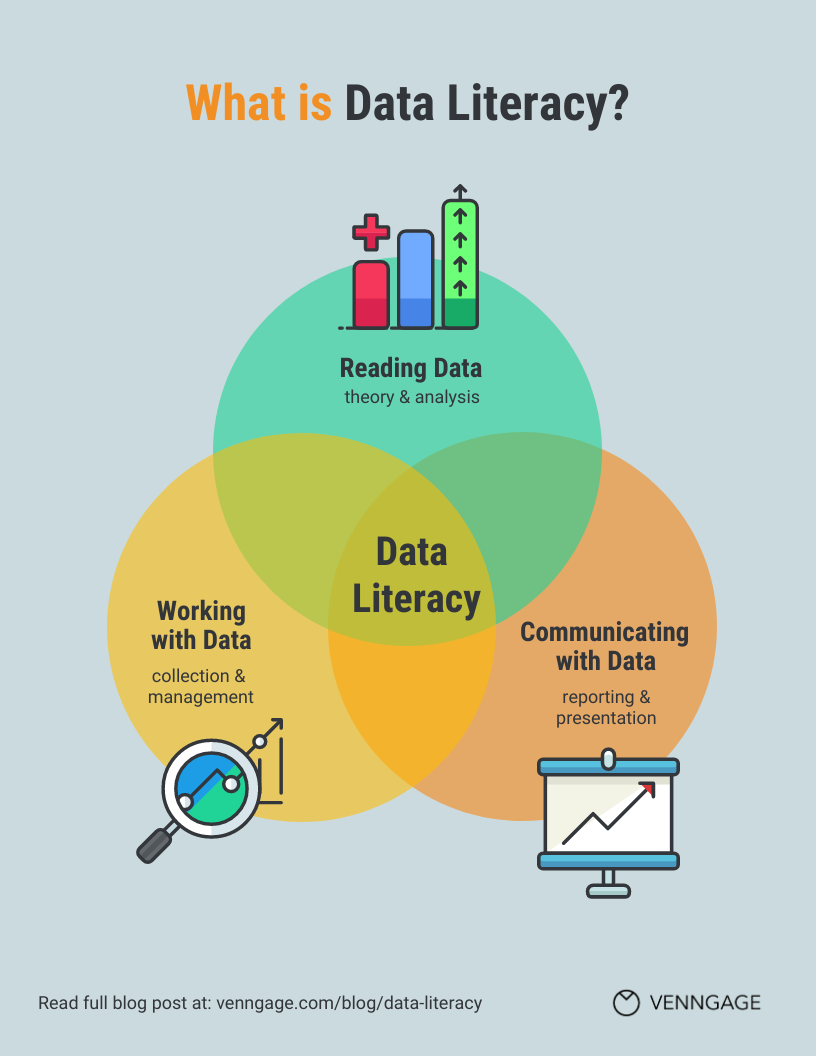
1. Reading Data: This aspect involves the ability to understand and interpret data. It includes skills such as:
- Data comprehension: Being able to understand the structure, format, and content of different types of data.
- Data analysis: Analyzing data to identify patterns, trends, and insights.
- Critical thinking: Evaluating the quality and reliability of data sources.
- Statistical literacy: Understanding basic statistical concepts and methods used in data analysis.
Reading data requires individuals to be able to interpret graphs, charts, tables, and other forms of data visualization
to extract meaningful information.
2. Working with Data: This aspect focuses on the ability to manipulate, process, and analyze data effectively. It includes skills such as:
- Data manipulation: Cleaning, organizing, and preparing data for analysis.
- Data mining: Extracting valuable insights and patterns from large datasets.
- Programming skills: Using programming languages like Python, R, or SQL to work with data.
- Database management: Understanding database systems and querying data from databases.
Working with data involves using tools and software for data analysis, such as Excel, Tableau, or Jupyter notebooks,
to perform various tasks like filtering, sorting, and aggregating data.
3. Communicating with Data: This aspect involves the ability to effectively communicate insights and findings derived from data analysis. It includes skills such as:
- Data visualization: Presenting data visually using charts, graphs, and dashboards to make it easier to understand.
- Storytelling: Crafting narratives around data to convey meaningful stories and insights.
- Data interpretation: Explaining the significance of data findings and their implications.
- Presentation skills: Communicating data insights effectively through presentations or reports.
Communicating with data requires individuals to be able to convey complex information in a clear, concise, and
compelling manner, tailored to different audiences.
https://venngage.com/blog/data-literacy/
Data Literacy: 7 Things Beginners Need to Know - Venngage
Are you confident you're data literate? Read to learn more about data literacy and 7 things beginners should know to build their data literacy skills.
venngage.com
Other perspectives of data literacy
1. Collection:
Collecting data is the first step. This can be quantitative or qualitative data. For example, data collected through surveys or experiments, data gathered from online platforms, or data extracted from internal systems within organizations.
2. Understanding:
Understanding the collected data is crucial. This involves grasping the structure, format, and meaning of the data. This can be achieved through the use of statistics, data analysis techniques, visualization techniques, etc.
3. Interpretation:
Interpreting data goes beyond collecting and understanding it. It involves discovering the messages or trends conveyed by the data and utilizing them for business or decision-making purposes.
4. Utilization:
The ultimate goal of data literacy is to utilize data to solve problems or make decisions. Using data to identify opportunities, solve problems, and enhance business performance is achieved through data literacy.
Data literacy is essential for both individuals and organizations to succeed. Properly collecting, understanding,
interpreting, and utilizing data are crucial skills for gaining a competitive edge in modern society.
'Study Note > Data Analysis' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Mece logic tree (0) | 2024.04.29 |
|---|---|
| AARRR Funnel Analysis (0) | 2024.04.24 |
| Qualitative Data vs Quantitatived Data (0) | 2024.04.24 |
| Sampling Bias and Sample Error (0) | 2024.04.24 |
| Simpson's paradox (0) | 2024.04.24 |


